import { } from "@effectionx/converge"@effectionx/converge
Recognize a desired state and synchronize on when that state has been achieved.
This package is a port of @bigtest/convergence adapted for Effection structured concurrency.
Why Convergence?
Let's say you want to write an assertion to verify a simple cause and effect: when a certain button is clicked, a dialog appears containing some text that gets loaded from the network.
In order to do this, you have to make sure that your assertion runs after the effect you're testing has been realized.
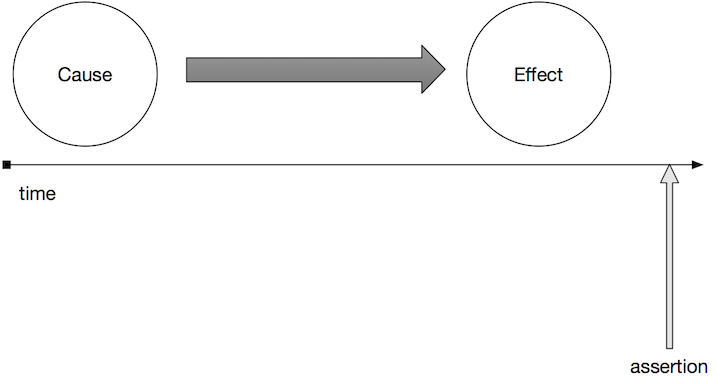
If not, then you could end up with a false negative, or "flaky test" because you ran the assertion too early. If you'd only waited a little bit longer, then your test would have passed. So sad!
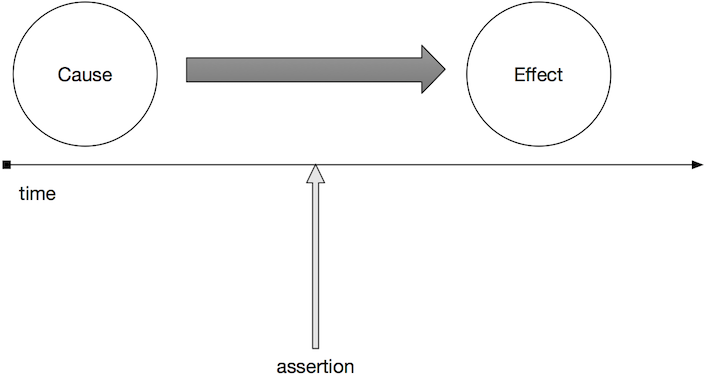
In fact, test flakiness is the reason most people shy away from writing big tests in JavaScript in the first place. It seems almost impossible to write robust tests without having visibility into the internals of your runtime so that you can manually synchronize on things like rendering and data loading. Unfortunately, those can be a moving target, and worse, they couple you to your framework.
But what if instead of trying to run our assertions at just the right time, we ran them many times until they either pass or we decide to give up?
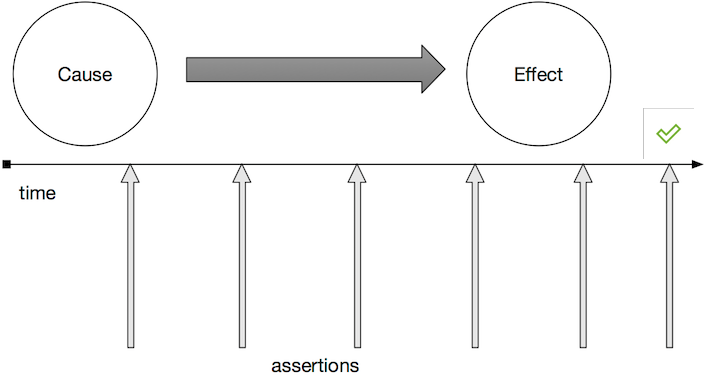
This is the essence of what @effectionx/converge provides:
repeatedly testing for a condition and then allowing code to run when
that condition has been met.
And it isn't just for assertions either. Because it is a general mechanism for synchronizing on any observed state, it can be used to properly time test setup and teardown as well.
Installation
npm install @effectionx/converge
Usage
when(assertion, options?)
Converges when the assertion passes within the timeout period. The
assertion runs repeatedly (every 10ms by default) and is considered
passing when it does not throw or return false. If it never passes
within the timeout, the operation throws with the last error.
import { when } from "@effectionx/converge";
// Wait for a condition to become true
let { value } = yield* when(function* () {
if (total !== 100) throw new Error("not ready");
return total;
});
// With custom timeout
yield* when(
function* () {
if (!element.isVisible) throw new Error("not visible");
},
{ timeout: 5000 },
);
always(assertion, options?)
Converges when the assertion passes throughout the timeout period.
Like when(), the assertion runs repeatedly, but it must pass
consistently for the entire duration. If it fails at any point, the
operation throws immediately.
import { always } from "@effectionx/converge";
// Verify a condition remains true
yield* always(function* () {
if (counter >= 100) throw new Error("counter exceeded limit");
});
// With custom timeout
yield* always(
function* () {
if (!connection.isAlive) throw new Error("connection lost");
},
{ timeout: 5000 },
);
Options
Both when and always accept an options object:
| Option | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
timeout | number | 2000 (when) / 200 (always) | Maximum time to wait in milliseconds |
interval | number | 10 | Time between assertion retries in milliseconds |
Stats Object
Both functions return a ConvergeStats object with timing and execution info:
interface ConvergeStats<T> {
start: number; // Timestamp when convergence started
end: number; // Timestamp when convergence ended
elapsed: number; // Milliseconds the convergence took
runs: number; // Number of times the assertion was executed
timeout: number; // The timeout that was configured
interval: number; // The interval that was configured
value: T; // The return value from the assertion
}
Example:
let stats = yield* when(
function* () {
return yield* fetchData();
},
{ timeout: 5000 },
);
console.log(`Converged in ${stats.elapsed}ms after ${stats.runs} attempts`);
console.log(stats.value); // the fetched data
Examples
Waiting for an element to appear
yield* when(function* () {
let element = document.querySelector('[data-test-id="dialog"]');
if (!element) throw new Error("dialog not found");
return element;
});
Verifying a value remains stable
yield* always(
function* () {
if (connection.status !== "connected") {
throw new Error("connection dropped");
}
},
{ timeout: 1000 },
);
Using with file system operations
import { when } from "@effectionx/converge";
import { access } from "node:fs/promises";
import { until } from "effection";
// Wait for a file to exist
yield* when(
function* () {
let exists = yield* until(
access(filePath).then(
() => true,
() => false,
),
);
if (!exists) throw new Error("file not found");
return true;
},
{ timeout: 10000 },
);
API Reference
Statistics about a convergence operation.
Type Parameters
T
Properties
- start: number
Timestamp when convergence started
- end: number
Timestamp when convergence ended
- elapsed: number
Milliseconds the convergence took
- runs: number
Number of times the assertion was executed
- timeout: number
The timeout that was configured
- interval: number
The interval that was configured
- value: T
The return value from the assertion
function when<T>(assertion: () => Operation<T>, options: ConvergeOptions = {}): Operation<ConvergeStats<T>>
Converges on an assertion by resolving when the given assertion
passes within the timeout period. The assertion will run repeatedly
at the specified interval and is considered to be passing when it
does not throw or return false.
If the assertion never passes within the timeout period, then the operation will throw with the last error received.
Examples
Example 1
Basic usage
// Wait for a value to become true
yield* when(function*() {
if (total !== 100) throw new Error(`expected 100, got ${total}`);
return total;
});
Example 2
With custom timeout
// Wait up to 5 seconds for file to exist
yield* when(function*() {
let exists = yield* until(access(filePath).then(() => true, () => false));
if (!exists) throw new Error("file not found");
return true;
}, { timeout: 5000 });
Example 3
Using the stats
let stats = yield* when(function*() {
return yield* until(readFile(path, "utf-8"));
}, { timeout: 1000 });
console.log(`Converged in ${stats.elapsed}ms after ${stats.runs} attempts`);
console.log(stats.value); // file content
Type Parameters
T
Parameters
assertion: () => Operation<T>
-
The assertion to converge on. Can be a generator function.
-
Configuration options
Return Type
Operation<ConvergeStats<T>>
Statistics about the convergence including the final value
function always<T>(assertion: () => Operation<T>, options: ConvergeOptions = {}): Operation<ConvergeStats<T>>
Converges on an assertion by resolving when the given assertion
passes consistently throughout the timeout period. The assertion
will run repeatedly at the specified interval and is considered
to be passing when it does not throw or return false.
If the assertion fails at any point during the timeout period, the operation will throw immediately with that error.
Examples
Example 1
Basic usage
// Ensure a value stays below 100 for 200ms
yield* always(function*() {
if (counter >= 100) throw new Error("counter exceeded limit");
});
Example 2
With custom timeout
// Verify connection stays alive for 5 seconds
yield* always(function*() {
if (!isConnected) throw new Error("connection lost");
}, { timeout: 5000 });
Type Parameters
T
Parameters
assertion: () => Operation<T>
-
The assertion to converge on. Can be a generator function.
-
Configuration options
Return Type
Operation<ConvergeStats<T>>
Statistics about the convergence including the final value
